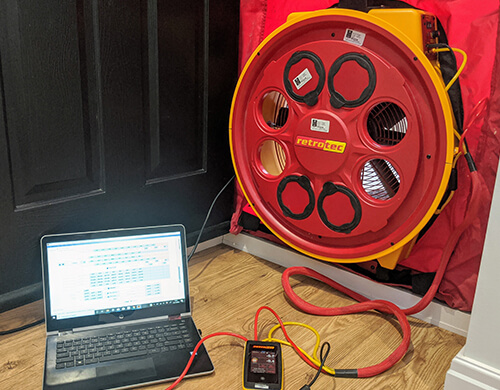
ATTMA Licensed Air Tightness Testing in Bedfordshire
Air tightness testing, also called air leakage testing or air pressure testing, calculates the quantity of air escaping through openings in a building. Air tightness testing has been a compulsory part of the building regulations for new dwellings, renovations and commercial projects since the revision of Document L in 2006.