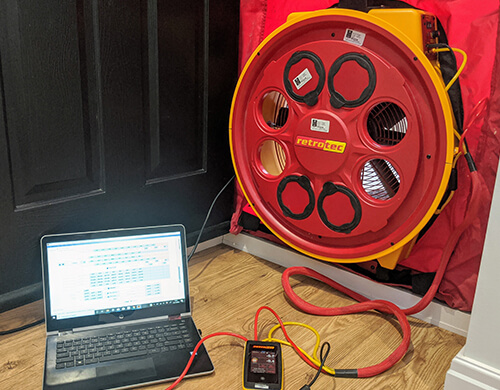
Air Tightness Testing, Certified by AF-Acoustics, in Knightsbridge
Air tightness testing, also called air leakage testing or air pressure testing, calculates the quantity of air escaping through openings in a building. Air tightness testing became an integral part of building regulations for new buildings, commercial developments and revamped buildings in 2006 after Document L was reviewed.